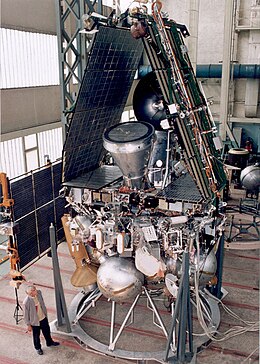
Mars 96
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
102852 characters 29 sections 24 paragraphs 11 images 331 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.114 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2017 |
123232 characters 29 sections 24 paragraphs 14 images 457 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.114 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2016 |
121812 characters 29 sections 24 paragraphs 14 images 454 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.114 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2015 |
108233 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 12 images 386 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.114 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2014 |
108240 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 12 images 386 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.114 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2013 |
108239 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 12 images 386 internal links 9 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.115 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean , Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2012 |
85398 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 8 images 255 internal links 8 external links |
penetrator 0.264 penetrators 0.261 96 0.250 forebody 0.225 burn 0.163 unit 0.161 stage 0.157 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.115 block 0.113 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2011 |
85222 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 8 images 254 internal links 8 external links |
penetrator 0.265 penetrators 0.261 96 0.251 forebody 0.225 burn 0.164 unit 0.161 stage 0.158 stations 0.154 afterbody 0.150 spacecraft 0.133 studies 0.125 propulsion 0.119 insertion 0.118 fourth 0.115 block 0.114 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2010 |
84025 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 7 images 251 internal links 7 external links |
penetrator 0.266 penetrators 0.263 96 0.232 forebody 0.227 burn 0.165 unit 0.162 stage 0.159 stations 0.155 afterbody 0.151 spacecraft 0.134 studies 0.126 propulsion 0.120 insertion 0.119 fourth 0.115 block 0.114 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2009 |
69291 characters 28 sections 24 paragraphs 8 images 142 internal links 7 external links |
penetrator 0.267 penetrators 0.263 96 0.232 forebody 0.227 burn 0.165 unit 0.162 stage 0.159 stations 0.155 afterbody 0.151 spacecraft 0.134 studies 0.126 propulsion 0.120 insertion 0.119 fourth 0.116 block 0.114 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was a Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile , and Bolivia . [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase. |
|
| 2008 |
63683 characters 27 sections 22 paragraphs 9 images 141 internal links 3 external links |
penetrator 0.330 forebody 0.250 penetrators 0.207 96 0.185 burn 0.181 unit 0.178 afterbody 0.166 studies 0.138 propulsion 0.132 insertion 0.131 fourth 0.127 cruise 0.119 astrophysical 0.115 stage 0.111 airbags 0.110 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was an orbiter launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by Russia and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 200-mile long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile, and Bolivia. [1] The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos vehicles launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. But for the Mars 96 probe the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos vehicle. Alas, the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe. |
|
| 2007 |
60326 characters 25 sections 19 paragraphs 9 images 141 internal links 2 external links |
penetrator 0.357 forebody 0.270 unit 0.193 afterbody 0.180 penetrators 0.179 burn 0.172 studies 0.150 propulsion 0.143 cruise 0.129 orbiter 0.125 96 0.125 astrophysical 0.124 airbags 0.119 phobos 0.117 spacecraft 0.115 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was an orbiter launched in 1996 by Russia and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. The orbiter's intended destination was Mars, but the probe ultimately crashed into the Pacific Ocean due to problems with the launch vehicle. The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos vehicles launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. But for the Mars 96 probe the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos vehicle. Alas, they did not get to find out if they had produced a successful design this time due to the launch vehicle failure. |
|
| 2006 |
59002 characters 25 sections 20 paragraphs 12 images 130 internal links 2 external links |
penetrator 0.359 forebody 0.272 unit 0.194 afterbody 0.181 penetrators 0.180 burn 0.173 studies 0.151 propulsion 0.144 cruise 0.130 96 0.126 astrophysical 0.125 airbags 0.120 phobos 0.118 orbiter 0.117 spacecraft 0.116 |
Mars 96 (sometimes called Mars 8 ) was an orbiter launched in 1996 by Russia and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos vehicles launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. But for the Mars 96 probe the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos vehicle. Alas, they did not get to find out if they had produced a successful design this time due to a launch vehicle failure. |
|
| 2005 |
6679 characters 2 sections 6 paragraphs 2 images 14 internal links 1 external links |
96 0.387 burned 0.253 block 0.240 penetrators 0.197 burn 0.162 propelled 0.159 tracked 0.155 orbit 0.154 stage 0.151 launched 0.144 trajectory 0.137 pacific 0.127 failed 0.124 timer 0.119 bolivia 0.119 |
Mars 96 was an orbiter launched in 1996 by Russia and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos vehicles launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. But for the Mars 96 probe the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos vehicle. Alas, they did not get to find out if they had produced a successful design this time. |
|
| 2004 |
3431 characters 0 sections 3 paragraphs 0 images 14 internal links 0 external links |
96 0.467 penetrators 0.278 launched 0.203 bolivia 0.168 stations 0.164 phobos 0.145 probe 0.138 1996 0.137 elliptical 0.137 orbit 0.135 flaws 0.131 trajectory 0.128 chile 0.121 complement 0.119 heaviest 0.119 |
Mars 96 was an orbiter launched in 1996 by Russia and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos vehicles launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. But for the Mars 96 probe the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos vehicle. Alas, they did not get to find out if they had produced a successful design this time. It was, however, a very ambitious mission and the heaviest interplanetary probe ever launched. It included a large complement of instruments, many provided by France , Germany , and other European countries (some of which have since been re-flown on Mars Express , launched in 2003). |